Uro-Health Hub
Your Evidence-Based Guide to Men's Sexual Health
Important Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always seek the advice of a qualified health provider for any medical concerns.
Knowledge Hub
reviewed by factbasedurology.com | Last updated: 06/02/2026
Interactive Research Map
Urological health is a complex system where different fields of study inform one another. This interactive map visualizes the critical links between major areas of scientific inquiry. Click and drag any node to explore these connections, and select a topic to view curated summaries of the latest significant research in that domain.
Explore the Research
Select a node on the graph to view summaries of recent and significant research in that area.
Cardiovascular Health
Sep 10, 2025
New research confirms that endothelial dysfunction is a common pathway for both ED and heart disease, reinforcing the penis as a "barometer" of systemic health.
Erectile Dysfunction
Aug 28, 2025
The AUA has updated its position on LiSWT, acknowledging growing evidence for its use in mild to moderate vasculogenic ED, though it remains investigational.
Gut Microbiome
Sep 5, 2025
A major study in *Nature Medicine* has linked gut bacteria diversity to serum testosterone levels, opening new avenues for research into probiotic therapies for hormonal health.
Hormonal Health
July 20, 2025
Research continues to show the wide-ranging effects of hypogonadism beyond libido, including impacts on mood, energy, and metabolic syndrome.
AI Diagnostics
Aug 15, 2025
A trial in *The Lancet* confirmed AI can read prostate MRIs with expert-level accuracy, promising to speed up diagnosis and reduce unnecessary biopsies in the future.
reviewed by factbasedurology.com | Last updated: 06/02/2026
Doctor's Visit Prep Tool
Use this tool to prepare for a productive conversation with your doctor. Select your concern, check off your symptoms and questions, and generate a printable summary to take with you.
2. Select Symptoms & Questions for ED
Common Symptoms
Questions to Ask
2. Select Symptoms & Questions for Prostate/Urinary Issues
Common Symptoms
Questions to Ask
reviewed by factbasedurology.com | Last updated: 06/02/2026
Patient Journey Roadmaps
Navigating a health concern can feel overwhelming. These roadmaps provide a clear, step-by-step guide through the typical journey, from understanding symptoms to long-term management.
A Roadmap for Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Step 1: Understanding Symptoms
Learn the science, causes, and what ED can signal about your overall health. Go to ED section →
Step 2: Preparing for a Doctor's Visit
Use our Prep Tool to generate a summary for a productive conversation. Go to Prep Tool →
Step 3: The Diagnostic Process
Understand the typical evaluation, including medical history, physical exams, and lab tests to find the root cause.
Step 4: Exploring Treatment Tiers
Review the evidence-based treatment options, from lifestyle changes to first-line and advanced therapies. See treatment options →
Step 5: Long-Term Wellness
Focus on maintaining cardiovascular health and the lifestyle factors that support long-term sexual function. Go to Pillars of Wellness →
reviewed by factbasedurology.com | Last updated: 06/02/2026
Interactive Anatomy Explorer
Click the pulsating hotspots on the diagram to learn about the key structures involved in male sexual and urinary health.
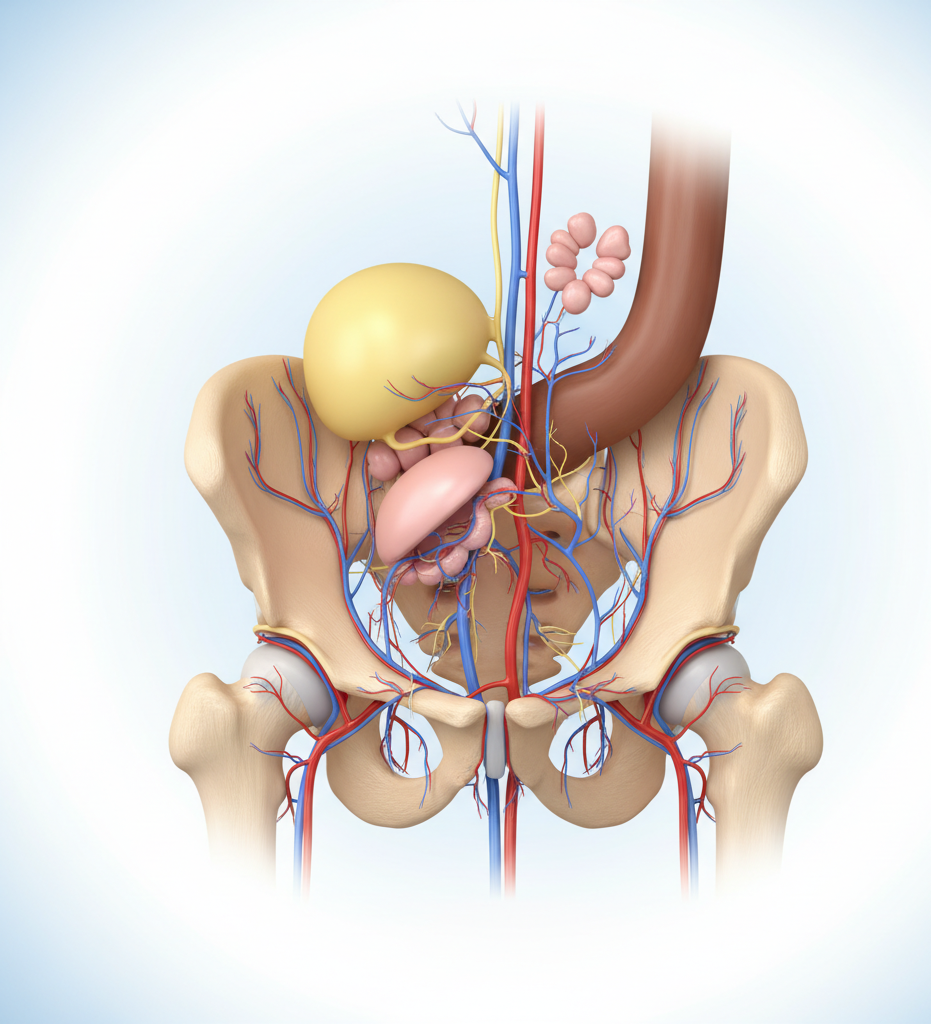
Select a structure to learn more.
Use this interactive tool to explore the complex, interconnected systems of the male pelvic region.
Corpora Cavernosa
These are the two sponge-like cylinders of erectile tissue that run along the upper side of the penis. During arousal, they fill with blood to produce a rigid erection. Their health is critical for erectile function.
Learn more about Erectile Dysfunction →Prostate Gland
A walnut-sized gland located below the bladder. It produces seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. Conditions like BPH (enlargement) can cause urinary issues.
Learn more about Prostate Health →Bladder
A muscular sac that stores urine. The prostate gland surrounds the urethra as it exits the bladder, which is why prostate enlargement can affect urination.
Learn more about Prostate Health →Testicle
The testicles (or testes) are responsible for producing both sperm and the primary male hormone, testosterone. Regular self-exams are vital for early detection of any abnormalities.
Learn more about Testicular Health →reviewed by factbasedurology.com | Last updated: 06/02/2026
The Modern Urological Perspective on Male Sexual Health
Our Philosophy: Evidence-Based Medicine (EBM)
The foundation of this hub is EBM: “the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of the current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients”.[7] We move away from anecdote and toward a framework where information is grounded in objective, systematic assessment of the best available scientific data, as championed by organizations like the American Urological Association (AUA) and European Association of Urology (EAU).
The Penis as a Barometer of Systemic Health
A central theme of modern andrology is that sexual health issues are often the first clinical sign of a more significant, underlying systemic disease. Erectile dysfunction (ED), for example, is now widely recognized as a "silent marker" for future cardiovascular disease.[9] The penile arteries are smaller than those of the heart, so the processes that cause heart attacks often manifest first as ED, sometimes years before a major cardiac event.[12] This elevates sexual health from a "lifestyle" issue to a critical indicator of overall well-being.
reviewed by factbasedurology.com | Last updated: 06/02/2026
The Pillars of Penile Wellness: Lifestyle and Systemic Factors
The evidence is unequivocal: penile health is inextricably linked to overall systemic health. The same lifestyle choices that protect your heart also protect your erections. Proactive, preventative wellness is the most effective strategy for maintaining long-term sexual function.
Increased Likelihood of ED by Risk Factor
The Data on Comorbidities
The link between ED and other conditions is well-documented. Clinical data shows a strong correlation: almost 50% of men with known coronary artery disease have significant ED, 40% of men with ED have hypertension, and 42% have high cholesterol.[12]
| Lifestyle Risk Factor | Mechanism of Action on Erectile Function | Supporting Statistics/Facts | Evidence-Based Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smoking | Induces vasoconstriction; causes direct damage to the endothelial lining of blood vessels, accelerating atherosclerosis.[9] | Quitting was associated with a 25% improvement in erectile quality after one year.[12] | Complete smoking cessation. |
| Obesity / High BMI | Associated with low testosterone, systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, and comorbidities like diabetes.[12] | Obesity is associated with a 50% increase in ED likelihood. 31% of obese men restored normal function after a two-year weight loss program.[12] | Maintain a healthy body weight and BMI. |
| Sedentary Lifestyle | Contributes to poor cardiovascular health, atherosclerosis, and obesity.[20] | Regular aerobic exercise improves erectile function.[19] Just 30 minutes of daily activity improves cardiovascular health.[18] | Engage in regular physical activity. |
| Poor Diet | A diet high in processed foods contributes to atherosclerosis, inflammation, and metabolic syndrome.[18] | A Mediterranean diet (rich in fruits, vegetables, fish) is shown to reduce ED risk.[18] | Adopt a heart-healthy diet. |
| Excessive Alcohol Use | Can cause direct toxicity to erectile tissue, nerve damage, and hormonal disruption.[12] | Heavy alcohol users report an increased risk of ED compared to the general population.[12] | Limit alcohol intake to moderate levels. |
reviewed by factbasedurology.com | Last updated: 06/02/2026
Erectile Dysfunction (ED): A Comprehensive Analysis
ED Prevalence by Age
Primary Causes of ED
Clinical Classifications of ED
- Vasculogenic: The most common cause, related to inadequate blood flow from conditions like atherosclerosis.
- Neurogenic: Caused by damage to the nerves that control the erectile process (e.g., from diabetes or surgery).
- Hormonal: Related to low testosterone (hypogonadism) or other hormonal imbalances.
- Psychogenic: Originating from psychological factors like performance anxiety, stress, or depression.
The Science of an Erection: A Bio-Chart
Stimulation
Nerve impulses trigger release of Nitric Oxide (NO) NO.
Relaxation
NO increases levels of cGMP cGMP, relaxing penile arteries.
Inflow & Trapping
Blood flows rapidly into erectile bodies, compressing veins to trap blood.
Return to Flaccid State
The enzyme PDE5 PDE5 breaks down cGMP. Oral ED meds work by inhibiting PDE5.
Comparing ED Treatment Efficacy Rates
Evidence-Based Treatment Tiers
| Tier | Treatment Modality | How It Works | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| First-Line | Lifestyle Changes & Oral PDE5 Inhibitors | Addressing risk factors is foundational. Oral drugs (e.g., Sildenafil) block the PDE5 enzyme, increasing blood flow in response to stimulation. | Meds require stimulation to work and are contraindicated with nitrates. Side effects can include headache and flushing. |
| Second-Line | Vacuum Devices & Injections (ICI) | A VED uses a vacuum to draw blood into the penis. ICI involves self-injecting a vasodilator directly into the erectile tissue. | ICI is highly effective but carries a risk of priapism (prolonged erection) and penile scarring. |
| Third-Line | Penile Prosthesis (Implant) | A surgical procedure to implant cylinders (malleable or inflatable) that provide mechanical rigidity. | An irreversible surgery with high patient satisfaction. Risks include infection and mechanical failure. |
reviewed by factbasedurology.com | Last updated: 06/02/2026
Premature Ejaculation (PE): Causes, Classification, and Control
PE is the most common male sexual dysfunction, characterized by ejaculation within about one minute of penetration, an inability to delay it, and resulting personal distress. A man not bothered by a short latency time does not have clinical PE.
The process involves two phases: Emission (semen is deposited into the urethra) and Expulsion (rhythmic contractions propel semen out).
The distress of PE can also affect relationships, as studies show partners of men with PE often report lower levels of sexual satisfaction.
PE Prevalence in Adult Men
Classification of PE
- Lifelong (Primary): Present since first sexual experiences. Often neurobiological.
- Acquired (Secondary): Develops later in life, often linked to medical (ED, prostatitis) or psychological causes.
- Variable & Subjective: Normal variations in performance or a man's perception of being too quick despite normal latency.
Clinical Management Strategies
Treatment is multi-modal, aiming to improve control and reduce distress. Options include behavioral therapies (the "start-stop" and "squeeze" techniques), topical anesthetics (creams/sprays) to reduce sensitivity, and oral medications like SSRIs, which can delay orgasm.
reviewed by factbasedurology.com | Last updated: 06/02/2026
Peyronie's Disease (PD): Understanding Penile Curvature
An acquired condition where scar tissue (plaque) in the tunica albuginea (the sheath around erectile bodies) causes the penis to bend, curve, or shorten during erection. It is often painful and can be associated with ED.
Peyronie's Disease Prevalence
Visualizing Peyronie's Disease
Normal Erection
The tunica albuginea stretches evenly, allowing for a straight erection.
Peyronie's Erection
The inelastic plaque does not stretch, causing a distinct bend at its location.
The Two Phases of Peyronie's
- Active (Acute) Phase: An ongoing inflammatory process, often with pain. The deformity may worsen. Can last 12-18 months.
- Stable (Chronic) Phase: Inflammation and pain subside, and the curvature stabilizes. Definitive treatment is only considered in this phase.
What Doesn't Work: AUA Guidelines
To combat misinformation, the American Urological Association explicitly recommends **AGAINST** the use of oral therapies such as Vitamin E, tamoxifen, or omega-3 fatty acids for Peyronie's, as there is no high-quality evidence to support their use.
reviewed by factbasedurology.com | Last updated: 06/02/2026
Prostate & Testicular Health
Prostate Health: BPH & Prostatitis
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), or an enlarged prostate, is a non-cancerous condition affecting up to 90% of men by age 85. It can cause urinary symptoms like a weak stream or frequent urination. Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate, often causing pelvic pain and is the most common urological issue in men under 50.
BPH Prevalence by Age
Testicular Health & Self-Exam
Testicular cancer is the most common cancer in men aged 15-34 but is highly curable when detected early. A monthly testicular self-exam is crucial for early detection.
How to Perform a Testicular Self-Exam
- Perform during or after a warm shower when the scrotal skin is relaxed.
- Examine one testicle at a time using both hands.
- Gently roll the testicle between the thumbs and fingers. Feel for any hard lumps, smooth rounded bumps, or changes in size, shape, or consistency.
- It's normal for one testicle to be slightly larger than the other.
- Report any new or unusual findings to your doctor promptly.
Testicular Cancer Peak Incidence
reviewed by factbasedurology.com | Last updated: 06/02/2026
Hormones & Male Fertility
Testosterone Deficiency (Hypogonadism)
Low testosterone is a medical condition that can cause more than just low libido. Symptoms can include fatigue, low mood, reduced muscle mass, and increased body fat. Diagnosis requires a morning blood test. After age 30, testosterone declines by about 1% per year on average.
Average Testosterone Decline by Age
Male Infertility
Male factors contribute to about half of all infertility cases. It is a separate issue from sexual dysfunction. Common causes include varicocele (enlarged veins in the scrotum), hormonal imbalances, or blockages in the reproductive tract.
Primary Causes of Male Infertility
reviewed by factbasedurology.com | Last updated: 06/02/2026
Broader Urological Health
While this hub focuses on sexual health, urology covers the entire male genitourinary system. Here is a brief overview of other common conditions.
Kidney Stones
Hard deposits of minerals and salts that form inside the kidneys. They can cause severe pain in the side and back (flank pain), blood in the urine, and nausea as they pass through the urinary tract.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
While less common in men than women, UTIs can occur and may indicate an underlying issue like an enlarged prostate. Symptoms include a painful or burning sensation during urination and a frequent urge to urinate.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
A crucial aspect of sexual health. Infections like HPV are a primary risk factor for penile cancer. Safe sex practices and regular testing are cornerstones of preventative health.
reviewed by factbasedurology.com | Last updated: 06/02/2026
Misinformation Watch
This section actively debunks common myths and misleading claims with verifiable scientific evidence.
Claim: "You can increase penis size with pills or exercises."
There is no scientific evidence that any pill, cream, or manual exercise (like "jelqing") can permanently increase penis size. These products are unregulated, and some can cause injury, scarring, and permanent damage. Cosmetic surgery is not endorsed by medical organizations and carries significant risks.[53]
Claim: "Sexual dysfunction is an inevitable part of aging."
While the prevalence of conditions like ED increases with age, it is not an unavoidable consequence of getting older. ED is often a symptom of underlying, and frequently treatable, health issues such as heart disease or diabetes. A healthy lifestyle and early medical intervention can manage and even prevent many age-related urological conditions.
Claim: "My partner is unsatisfied with my penis size."
Anxiety about penis size is overwhelmingly a psychological phenomenon driven by male self-perception. One landmark review found that while 84% of women report being satisfied with their partner's size, only 55% of men are satisfied with their own.[53] This shows the desire for a larger penis is driven by self-consciousness, not partner dissatisfaction.
reviewed by factbasedurology.com | Last updated: 06/02/2026
Research & Verification Hub
Our philosophy is grounded in Evidence-Based Medicine (EBM): the conscientious and judicious use of current best evidence in healthcare. This hub is designed to give you direct access to the facts.
Comparing ED Treatments: Efficacy vs. Invasiveness
Dictionary of Urological Terms
Emerging & Investigational Therapies
You may see information online about newer therapies. It is vital to understand the current evidence:
- Low-Intensity Shockwave Therapy (LiSWT): This therapy applies low-energy sound waves to the penis to promote blood vessel growth. While some studies are promising, it is still considered investigational by the AUA and EAU and is not yet a standard recommended treatment.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) & Stem Cells: These involve injecting a patient's own concentrated platelets or stem cells to rejuvenate tissue. These are highly experimental therapies for ED with insufficient evidence to support their routine use.
Understanding Clinical Trials
Medical treatments are tested in phases to ensure they are safe and effective:
- Phase I: Small trials to evaluate safety, dosage, and side effects.
- Phase II: Larger trials to assess effectiveness and further evaluate safety.
- Phase III: Large-scale trials to confirm effectiveness, monitor side effects, and compare to standard treatments. Most investigational therapies are in this phase.
- Phase IV: Post-marketing studies to gather more information on long-term risks and benefits.
Featured Study Deep Dive
Weight Loss and Erectile Function (The LOOK AHEAD Trial)
A sub-study of the landmark LOOK AHEAD trial provided strong evidence for lifestyle intervention. It found that 31% of obese men with ED who participated in a two-year intensive weight loss and exercise program regained normal erectile function, compared to only a small fraction in the control group.[12]
Methodology: This was a large, randomized controlled trial (RCT), the gold standard of evidence.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that significant, structured lifestyle changes can be a powerful and effective treatment for reversing ED in obese men.
reviewed by factbasedurology.com | Last updated: 06/02/2026
Scientific References
This page contains the full list of scientific and medical sources used to create the content on this hub. Click "View Source" to access the original study or guideline.
- Sackett DL, et al. Evidence based medicine: what it is and what it isn't. BMJ. 1996. View Source
- Salonia A, et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Sexual and Reproductive Health. EAU Guidelines Office; 2025. View Source
- Fung MM, et al. Heart disease risk factors predict erectile dysfunction 25 years later. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004. View Source
- Mykoniatis I, et al. Sexual Dysfunction Among Young and Middle-Aged Men. J Sex Med. 2020. View Source
- Silva AB, et al. Physical activity and exercise for erectile dysfunction. Br J Sports Med. 2017. View Source
- Janiszewski PM, et al. Abdominal obesity and physical inactivity are associated with erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2009. View Source
- Mondaini N, et al. The EAU-endorsed comprehensive guide to male sexual and reproductive health. Eur Urol. 2022. View Source
Evidence Snapshot
Source: ${source}
Sample: ${sample}
Method: ${methodology}
View full reference → `; const rect = e.target.getBoundingClientRect(); tooltipBox.style.left = `${rect.left + window.scrollX}px`; tooltipBox.style.top = `${rect.bottom + window.scrollY + 10}px`; if (rect.top > window.innerHeight / 2) { tooltipBox.style.top = `${rect.top + window.scrollY - tooltipBox.offsetHeight - 10}px`; } tooltipBox.style.visibility = 'visible'; tooltipBox.style.opacity = '1'; });el.addEventListener('mouseleave', () => { tooltipBox.style.visibility = 'hidden'; tooltipBox.style.opacity = '0'; }); }); }const chartInstances = {};window.initChartsForTab = function(tabID) { const chartsToInit = { 'wellness': ['lifestyleRiskChart'], 'ed': ['edPrevalenceChart', 'edCausesChart', 'edTreatmentEfficacyChart'], 'pe': ['pePrevalenceChart'], 'peyronies': ['peyroniesPrevalenceChart'], 'prostate_testicular': ['bphPrevalenceChart', 'testicularCancerAgeChart'], 'hormones': ['testosteroneDeclineChart', 'infertilityChart'], 'myths': ['perceptionGapChart'], 'research': ['efficacyVsInvasivenessChart'], 'latest_research': ['network-canvas'] };if (chartsToInit[tabID]) { chartsToInit[tabID].forEach(chartId => { if (!chartInstances[chartId]) { const canvas = document.getElementById(chartId); if (canvas) { if(chartId === 'network-canvas') { initializeNetworkGraph(canvas); } else { initializeChart(chartId); } chartInstances[chartId] = true; } } }); } } function initializeChart(chartId) { const chartConfigs = { 'edPrevalenceChart': { type: 'bar', data: { labels: ['Age 40', 'Age 70'], datasets: [{ label: '% of Men with some degree of ED', data: [40, 70], backgroundColor: ['#60a5fa', '#2563eb'], borderColor: ['#3b82f6', '#1d4ed8'], borderWidth: 1 }] }, options: { scales: { y: { beginAtZero: true, max: 100, ticks: { callback: value => value + '%' } } }, plugins: { legend: { display: false } } } }, 'edCausesChart': { type: 'pie', data: { labels: ['Organic (Physical) Causes', 'Psychogenic Causes'], datasets: [{ label: 'Primary Cause of ED', data: [80, 20], backgroundColor: ['#38bdf8', '#fbbf24'], borderColor: ['#0ea5e9', '#f59e0b'], borderWidth: 1 }] }, options: { responsive: true, maintainAspectRatio: true } }, 'bphPrevalenceChart': { type: 'bar', data: { labels: ['By Age 60', 'By Age 85'], datasets: [{ label: '% of Men with BPH', data: [50, 90], backgroundColor: ['#f9a8d4', '#ec4899'], borderColor: ['#f472b6', '#db2777'], borderWidth: 1 }] }, options: { scales: { y: { beginAtZero: true, max: 100, ticks: { callback: value => value + '%' } } }, plugins: { legend: { display: false } } } }, 'perceptionGapChart': { type: 'bar', data: { labels: ["Women's Satisfaction", "Men's Self-Satisfaction"], datasets: [{ label: 'Satisfaction Rate', data: [84, 55], backgroundColor: ['#34d399', '#f87171'], borderColor: ['#10b981', '#ef4444'], borderWidth: 1 }] }, options: { indexAxis: 'y', scales: { x: { beginAtZero: true, max: 100, ticks: { callback: value => value + '%' } } }, plugins: { legend: { display: false } } } }, 'lifestyleRiskChart': { type: 'bar', data: { labels: ['Obesity', 'Smoking'], datasets: [{ label: 'Increased Likelihood of ED', data: [50, 50], backgroundColor: ['#fb923c', '#f97316'], borderColor: ['#f97316', '#ea580c'], borderWidth: 1 }] }, options: { indexAxis: 'y', scales: { x: { beginAtZero: true, max: 100, ticks: { callback: value => '+' + value + '%' } } }, plugins: { legend: { display: false } } } }, 'pePrevalenceChart': { type: 'doughnut', data: { labels: ['Affected by PE', 'Not Affected'], datasets: [{ label: 'PE Prevalence', data: [25, 75], backgroundColor: ['#f472b6', '#e9d5ff'], borderColor: ['#db2777', '#d8b4fe'], borderWidth: 1 }] }, options: { responsive: true, maintainAspectRatio: true } }, 'infertilityChart': { type: 'pie', data: { labels: ['Varicocele', 'Hormonal Issues', 'Obstruction', 'Other/Unknown'], datasets: [{ label: 'Causes of Male Infertility', data: [40, 15, 10, 35], backgroundColor: ['#a78bfa', '#c4b5fd', '#818cf8', '#e5e7eb'], borderColor: '#ffffff', borderWidth: 2 }] }, options: { responsive: true, maintainAspectRatio: true } }, 'testicularCancerAgeChart': { type: 'bar', data: { labels: ['15-34', '35-54', '55+'], datasets: [{ label: 'Peak Incidence Age Range', data: [80, 15, 5], backgroundColor: ['#ef4444', '#f97316', '#facc15'], borderColor: ['#dc2626', '#ea580c', '#eab308'], borderWidth: 1 }] }, options: { scales: { y: { beginAtZero: true, ticks: { display: false } } }, plugins: { legend: { display: false }, tooltip: { callbacks: { label: (ctx) => ` Highest risk in the ${ctx.label} age group.` } } } } }, 'edTreatmentEfficacyChart': { type: 'bar', data: { labels: ['Oral Meds (PDE5i)', 'Injections (ICI)', 'Implants'], datasets: [{ label: 'Typical Efficacy/Satisfaction Rate', data: [70, 85, 95], backgroundColor: ['#2dd4bf', '#38bdf8', '#818cf8'], borderColor: ['#14b8a6', '#0ea5e9', '#6366f1'], borderWidth: 1 }] }, options: { scales: { y: { beginAtZero: true, max: 100, ticks: { callback: value => value + '%' } } }, plugins: { legend: { display: false } } } }, 'testosteroneDeclineChart': { type: 'line', data: { labels: ['30', '40', '50', '60', '70'], datasets: [{ label: 'Average Testosterone Level (Normalized)', data: [100, 90, 80, 70, 60], fill: true, backgroundColor: 'rgba(236, 72, 153, 0.1)', borderColor: '#ec4899', tension: 0.1 }] }, options: { scales: { y: { beginAtZero: false, ticks: { callback: value => value + '%' } } }, plugins: { legend: { display: false } } } }, 'efficacyVsInvasivenessChart': { type: 'scatter', data: { datasets: [ { label: 'Lifestyle / Oral Meds', data: [{x: 1, y: 70}], backgroundColor: '#2dd4bf', pointRadius: 10, pointHoverRadius: 12 }, { label: 'Vacuum Devices', data: [{x: 2, y: 80}], backgroundColor: '#38bdf8', pointRadius: 10, pointHoverRadius: 12 }, { label: 'Injections (ICI)', data: [{x: 3, y: 85}], backgroundColor: '#818cf8', pointRadius: 10, pointHoverRadius: 12 }, { label: 'Penile Implants', data: [{x: 4, y: 95}], backgroundColor: '#c084fc', pointRadius: 10, pointHoverRadius: 12 } ] }, options: { scales: { x: { title: { display: true, text: 'Level of Invasiveness' }, min: 0, max: 5, ticks: { stepSize: 1, callback: (val) => ['','Low', '', 'Medium', 'High', ''][val] } }, y: { title: { display: true, text: 'Efficacy / Satisfaction Rate' }, min: 50, max: 100, ticks: { callback: val => val + '%' } } }, plugins: { tooltip: { callbacks: { label: (ctx) => ` ${ctx.dataset.label}: ~${ctx.raw.y}% Efficacy` } }, legend: { display: true } } } }, 'peyroniesPrevalenceChart': { type: 'doughnut', data: { labels: ['Affected (est. 3-9%)', 'Not Affected'], datasets: [{ label: 'Peyronie\'s Prevalence', data: [6, 94], backgroundColor: ['#f43f5e', '#fce7f3'], borderColor: ['#be123c', '#fbcfe8'], borderWidth: 1 }] }, options: { responsive: true, maintainAspectRatio: true, plugins: { tooltip: { callbacks: { label: (ctx) => ` ${ctx.label}` } } } } } }; const config = chartConfigs[chartId]; if(config) { new Chart(document.getElementById(chartId), config); } }function initializeNetworkGraph(canvas) { const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d'); let nodes = [ { id: 'cardio', label: 'CV Health', color: '#ef4444', radius: 50, x: 0, y: 0, vx:0, vy:0 }, { id: 'ed', label: 'ED', color: '#3b82f6', radius: 50, x: 0, y: 0, vx:0, vy:0 }, { id: 'gut', label: 'Gut Biome', color: '#8b5cf6', radius: 45, x: 0, y: 0, vx:0, vy:0 }, { id: 'hormones', label: 'Hormones', color: '#ec4899', radius: 55, x: 0, y: 0, vx:0, vy:0 }, { id: 'ai', label: 'AI', color: '#14b8a6', radius: 40, x: 0, y: 0, vx:0, vy:0 } ]; const links = [ { source: 'cardio', target: 'ed' }, { source: 'ed', target: 'hormones' }, { source: 'gut', target: 'hormones' }, { source: 'cardio', target: 'hormones' } ]; let width, height, activeNodeId = 'cardio', draggedNode = null, hoveredNode = null;function initNetwork() { const container = canvas.parentElement; width = container.clientWidth; height = container.clientHeight; canvas.width = width; canvas.height = height; nodes.forEach(n => { n.x = width/2 + Math.random()*20-10; n.y = height/2 + Math.random()*20-10; }); canvas.updateActiveNode(activeNodeId); }function simulate() { const repulsion = -1000, attraction = 0.03, linkDist = 180, damping = 0.9; nodes.forEach(nodeA => { nodes.forEach(nodeB => { if (nodeA === nodeB) return; const dx = nodeB.x - nodeA.x, dy = nodeB.y - nodeA.y; let dist = Math.sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy); if (dist === 0) { dist = 1; } const force = repulsion / (dist*dist); nodeA.vx += (dx/dist) * force; nodeA.vy += (dy/dist) * force; }); }); links.forEach(l => { const src = nodes.find(n=>n.id===l.source), tgt = nodes.find(n=>n.id===l.target); const dx = tgt.x - src.x, dy = tgt.y - src.y; const dist = Math.sqrt(dx*dx+dy*dy); const force = (dist - linkDist) * attraction; const fx = (dx/dist)*force, fy = (dy/dist)*force; src.vx += fx; src.vy += fy; tgt.vx -= fx; tgt.vy -= fy; }); nodes.forEach(node => { if (node !== draggedNode) { node.x += node.vx; node.y += node.vy; node.vx *= damping; node.vy *= damping; node.x = Math.max(node.radius, Math.min(width - node.radius, node.x)); node.y = Math.max(node.radius, Math.min(height - node.radius, node.y)); } }); }function draw() { ctx.clearRect(0, 0, width, height); const isHovering = hoveredNode !== null; const connectedToHover = links.filter(l => l.source === hoveredNode?.id || l.target === hoveredNode?.id);links.forEach(l => { const src = nodes.find(n=>n.id===l.source), tgt = nodes.find(n=>n.id===l.target); const isLinked = isHovering && (connectedToHover.some(cl => (cl.source === src.id && cl.target === tgt.id) || (cl.source === tgt.id && cl.target === src.id))); ctx.beginPath(); ctx.moveTo(src.x, src.y); ctx.lineTo(tgt.x, tgt.y); ctx.strokeStyle = isLinked ? 'var(--color-accent)' : '#cbd5e1'; ctx.lineWidth = isLinked ? 2.5 : 1.5; ctx.globalAlpha = isHovering && !isLinked ? 0.2 : 0.8; ctx.stroke(); }); ctx.globalAlpha = 1.0;nodes.forEach(node => { const isHovered = node === hoveredNode; const isActive = node.id === activeNodeId; const isConnected = isHovering && (connectedToHover.some(l => l.source === node.id || l.target === node.id) || isHovered); ctx.beginPath(); ctx.arc(node.x, node.y, node.radius, 0, 2 * Math.PI); ctx.fillStyle = node.color; ctx.globalAlpha = isHovering && !isConnected ? 0.2 : 1.0; ctx.fill(); if (isActive || isHovered) { ctx.strokeStyle = 'var(--color-accent)'; ctx.lineWidth = 4; ctx.stroke(); } ctx.fillStyle = 'white'; ctx.font = 'bold 13px Montserrat, sans-serif'; ctx.textAlign = 'center'; ctx.textBaseline = 'middle'; ctx.fillText(node.label, node.x, node.y); }); ctx.globalAlpha = 1.0; }canvas.updateActiveNode = (id) => { activeNodeId = id; draw(); }; function loop() { if(!draggedNode) simulate(); draw(); networkAnimationId = requestAnimationFrame(loop); } initNetwork(); loop(); let offsetX, offsetY; canvas.addEventListener('mousedown', e => { const rect = canvas.getBoundingClientRect(), mouseX = e.clientX-rect.left, mouseY = e.clientY-rect.top; draggedNode = nodes.find(n => Math.sqrt((mouseX-n.x)**2 + (mouseY-n.y)**2) < n.radius); if (draggedNode) { offsetX = mouseX-draggedNode.x; offsetY = mouseY-draggedNode.y; showNetworkInfo(draggedNode.id); } }); canvas.addEventListener('mousemove', e => { const rect = canvas.getBoundingClientRect(), mouseX = e.clientX-rect.left, mouseY = e.clientY-rect.top; if (draggedNode) { draggedNode.x = mouseX - offsetX; draggedNode.y = mouseY - offsetY; } hoveredNode = nodes.find(n => Math.sqrt((mouseX-n.x)**2 + (mouseY-n.y)**2) < n.radius) || null; }); canvas.addEventListener('mouseup', () => { draggedNode = null; }); window.addEventListener('resize', initNetwork); }// --- DYNAMIC DATE LOGIC --- function setDynamicDate() { const today = new Date(); const dd = String(today.getDate()).padStart(2, '0'); const mm = String(today.getMonth() + 1).padStart(2, '0'); //January is 0! const yyyy = today.getFullYear(); const formattedDate = dd + '/' + mm + '/' + yyyy; document.querySelectorAll('.dynamic-date').forEach(el => el.textContent = formattedDate); }document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => { setDynamicDate(); document.getElementById('latest_research').style.display = 'block'; setupTooltips(); initChartsForTab('latest_research');const dictionaryList = document.getElementById('dictionary-list'); const searchInput = document.getElementById('dictionary-search'); const dictionaryTerms = { 'Androgen': 'A group of hormones that play a role in male traits and reproductive activity. The most well-known is testosterone.', 'Andrology': 'The medical subspecialty that focuses on male health, particularly male reproductive and sexual function.', 'Atherosclerosis': 'The hardening and narrowing of arteries due to plaque buildup. A primary cause of vascular erectile dysfunction.', 'Balanitis': 'Inflammation of the glans (head of the penis).', 'Balanitis Xerotica Obliterans (BXO)': 'A chronic inflammatory skin condition that can cause the foreskin to become scarred and tight (pathological phimosis). Also known as lichen sclerosus.', 'Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)': 'A non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, common in aging men, which can cause urinary problems.', 'Corpora Cavernosa': 'The two sponge-like cylinders of erectile tissue that run along the upper side of the penis and fill with blood to produce an erection.', 'Corpus Spongiosum': 'The third, smaller cylinder of erectile tissue that is located on the underside of the penis and contains the urethra.', 'cGMP': 'A molecule that relaxes smooth muscles in penile arteries, allowing blood to flow in. PDE5 inhibitors work by preventing its breakdown.', 'Detumescence': 'The process of an erection subsiding and the penis returning to a flaccid state.', 'Endothelial Dysfunction': 'A condition where the inner lining of blood vessels (the endothelium) doesn\'t function properly, impairing blood flow. A key factor in atherosclerosis and ED.', 'Glans': 'The medical term for the rounded head of the penis.', 'Hypogonadism': 'A medical condition in which the body doesn\'t produce enough testosterone.', 'Intracavernosal Injections (ICI)': 'A treatment for ED where medication is injected directly into the corpora cavernosa to produce an erection.', 'Intravaginal Ejaculatory Latency Time (IELT)': 'A clinical measure of the time from penetration to ejaculation, used in diagnosing PE.', 'Libido': 'The term for sexual desire or sex drive.', 'Nitric Oxide (NO)': 'A key neurotransmitter that initiates the erection process by triggering the relaxation of smooth muscle in penile arteries.', 'Nocturia': 'The need to wake and pass urine at night. A common symptom of BPH.', 'Paraphimosis': 'A medical emergency where a retracted foreskin becomes trapped behind the glans and cannot be returned to its normal position.', 'PDE5 Inhibitors': 'A class of oral medications (e.g., Sildenafil) that are a first-line treatment for ED. They work by blocking the PDE5 enzyme.', 'Penile Duplex Doppler Ultrasound': 'A specialized imaging test that uses sound waves to measure blood flow velocity in the penile arteries, helping to diagnose vasculogenic ED.', 'Penile Dysmorphophobia': 'A psychological condition where an individual has an obsessive, pathological belief that their penis is abnormally small, despite being of normal size.', 'Phimosis': 'The inability to retract the foreskin. It is normal in infants (physiological) but can be an acquired medical issue in adults (pathological).', 'Prepuce': 'The medical term for the foreskin.', 'Priapism': 'A prolonged, often painful erection lasting more than four hours without sexual stimulation. It is a medical emergency.', 'Prostatitis': 'Inflammation of the prostate gland, which can cause pelvic pain and urinary symptoms.', 'Smegma': 'A natural, cheese-like substance that can accumulate under the foreskin, composed of shed skin cells and oils.', 'Tunica Albuginea': 'The tough, fibrous sheath surrounding the corpora cavernosa. Scar tissue (plaque) in this sheath causes Peyronie\'s disease.', 'Urethra': 'The tube that carries both urine and semen out of the body through the penis.', 'Varicocele': 'An enlargement of the veins within the scrotum, similar to a varicose vein. It is a common cause of male infertility.', 'Veno-occlusive mechanism': 'The process of compressing veins against the tunica albuginea during an erection to trap blood in the corpora cavernosa, which is crucial for achieving rigidity.' }; function renderDictionary(filter = '') { dictionaryList.innerHTML = ''; const filteredKeys = Object.keys(dictionaryTerms).filter(key => key.toLowerCase().includes(filter.toLowerCase())); if (filteredKeys.length === 0) { dictionaryList.innerHTML = 'No terms found.
'; return; } filteredKeys.sort().forEach(key => { const dt = document.createElement('dt'); dt.className = 'font-semibold font-heading'; dt.textContent = key; const dd = document.createElement('dd'); dd.className = 'text-slate-600 pl-4'; dd.textContent = dictionaryTerms[key]; dictionaryList.appendChild(dt); dictionaryList.appendChild(dd); }); } searchInput.addEventListener('input', (e) => renderDictionary(e.target.value)); renderDictionary(); }); })();